Admissions are in progress for the AY 2020-2021 Batch
681fe1af8511e
Rapid technological developments and large scale mechanization in Petrochemical, Chemical, Engineering Industries, Construction Activities, etc. have resulted in complex safety & health problems in these industries. Hence these industries need the services of qualified safety professionals exclusively to take care of various safety and health aspects of their personnel/other persons who are likely to be affected by any adverse effects arising from these Industries.
Aim of this Course
- To induce lifelong learning knowledge skills, attitudes for social & personal development.
- To provide trained Human Resource.
- To provide leadership qualities.
- To create awareness of “The Quality of Life Protection” through Safety, Health, and Environment.
- To create awareness of hazards & operational hazards.
- To assist in the development of new methods & processes of Safety, Health and Environment skills, and analytical techniques.
- To develop managerial abilities and analytical skills, training, communicate with the community and interaction with government and statutory authorities
- To train the people concerned.

content1
WHY CONNECTIT
- From 2009 to 2020 Trained 806+ Candidates in Industrial Safety Course
- In academic year 2019 -2020, 81 Candidates undergoing training
- 98% Placement Record
- Sound Knowledge Faculty
- A/c Class Rooms with Wi-Fi enabled campus
- Online Classes
- Only one Institute in Telangana i.e. affiliated to SBTET, Govt. of TS
- Weekly examinations || Assignments ||Bio-metric Attendance ||Course Fee installment facility || Digital Payments only
- Excellent Library (Including Digital Library also) Contains Journals like NSC, LPA, Asian-Pacific Newsletters, IJOEM (International & India), Latest Indian Standards, Latest editions of Acts / Laws pertaining to HSE field, Books containing 500+ on OH&S Field, Excellent Video Library
- Practical exercises on Hazard Identification and Risk Assessment Techniques like HAZOP, HAZAN, JSA, PHA, FMEA, MCAA and Risk assessment as per MSIHC Rules, 1989
- Practical demonstration of Fire Hydrant and Fire Extinguishers, SCBA etc
- Industrial Visits
- Mock Interviews with experts in OH&S Field
- Internship in Industries (for fresh graduates)
- 100% placement assurance
- Special Classes on Soft skills for students like Coordinating for OH&S, Decision making for OH&S, Communication for OH&S, Conflict and Frustration Handling etc
STATUTORY REQUIREMENTS:
ACCORDING TO THE FACTORIES ACT, 1948 S/U 40B and AP/TS FACTORIES RULES, 1950 R/U 61(A) any manufacturing process/industries dealing with hazardous process shall employ one or more safety officers based on the company size.
The industrial safety course offered by ConnectIT Solutions is a recognized statutory qualification for appointment of Safety Officers as per the Factories Act, 1948.
DURATION: 1 YEAR, FULL TIME REGULAR
Eligibility Criteria
BSc.(Physics/Chemistry) with one year experience
(OR)
Any Diploma in Engineering/Technology with two-year relevant experience
(OR)
B.Tech. (Engineering/Technology) – Fresher’s / Experience
Faculty
The faculty consists of experts from Institutes, Specialists from Industries and Government Departments
681fe1af8b6df
METHODOLOGY
The course will be conducted through lectures, discussions, case studies, laboratory exercises, relevant film shows and factory visits. The students are also required to carry out one project work during the course of the programme, as a requirement under the Syllabus.
COURSE OUTLINE
EXAMINATION
All students will have to appear for a final examination, which will be conducted by the Board of Technical Education & Training, Govt. of Telangana
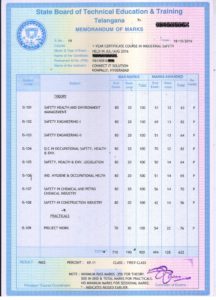
SAMPLE CERTIFICATE AND MEMO
For More Details
Testimonials

Vijay Kumar AP
I am a 9th batch industrial safety candidate. Completed course successfully and got job in MNC. I have completed first safety course in same institute in the year 2013. From 2013 connectit given a support to me in my career. Faculty are excellent.

Bharath Ghanta
Really a good institute for industrial safety training for safety and EHS professional career...

Chandrakanth K
good faculty available. internship facility available for Freshers. connectit giving 100% placement assistance.ibhave completed Industrial safety course in Ay 2014-2015 after that I got job in MNC.

Murali Manthena
I am 7th batch student of Industrial Safety course. After completion of B.Tech Civil i joined in this course. For internship we went to Hetero labs kazipally unit. After completion of course i placed in MNC

Anvesh Madineni
I have attended First aid training program conducted by ConnectIT. Good and super faculty explained well

G Chandrasekhar Reddy
Connect it solutions is the best institute for Industrial safety course, I was passed out from IS06 batch. They have excellent faculty to provide quality of education. If you are goingto choose careers in safety department blindly Join in Connect it solutions

B JOHNSON
I completed Diploma in INDUSTRIAL SAFETY and passed in First class. The management has the best faculty who have vast experience in Safety and they provide internship during the course period which helps in gaining more knowledge.
Clients